

Analyzing communication performance in Direct-to-Cell (D2C) and NTN environments is inherently complex due to continuously changing satellite orbit, geometry, and RF conditions throughout a satellite pass. Interpreting UE measurement logs solely at the KPI level is insufficient to explain why connectivity is established, maintained, or lost. Effective analysis requires correlation of measurement data with satellite motion and observation conditions along common time and spatial axes.
XCAP provides an analysis environment that correlates UE measurement data with satellite orbit, geometry, and Doppler behavior, enabling condition-based interpretation of connectivity behavior in NTN environments. This approach allows complex satellite connectivity phenomena to be analyzed beyond standalone KPI outcomes, focusing instead on the conditions under which they occur.
1. Satellite KPI Visualization
XCAP automatically reconstructs satellite position, orbit, and observation KPIs for past measurements based on recorded satellite communication data. This enables examination of satellite environment conditions and communication quality at the exact time of measurement within a unified analysis view.
Such visualization allows RF KPIs to be interpreted not as isolated performance values, but in the context of the satellite’s elevation and azimuth at the time of observation. As a result, identical KPI values can be distinguished based on differing satellite geometry conditions, supporting more accurate interpretation of connectivity behavior.
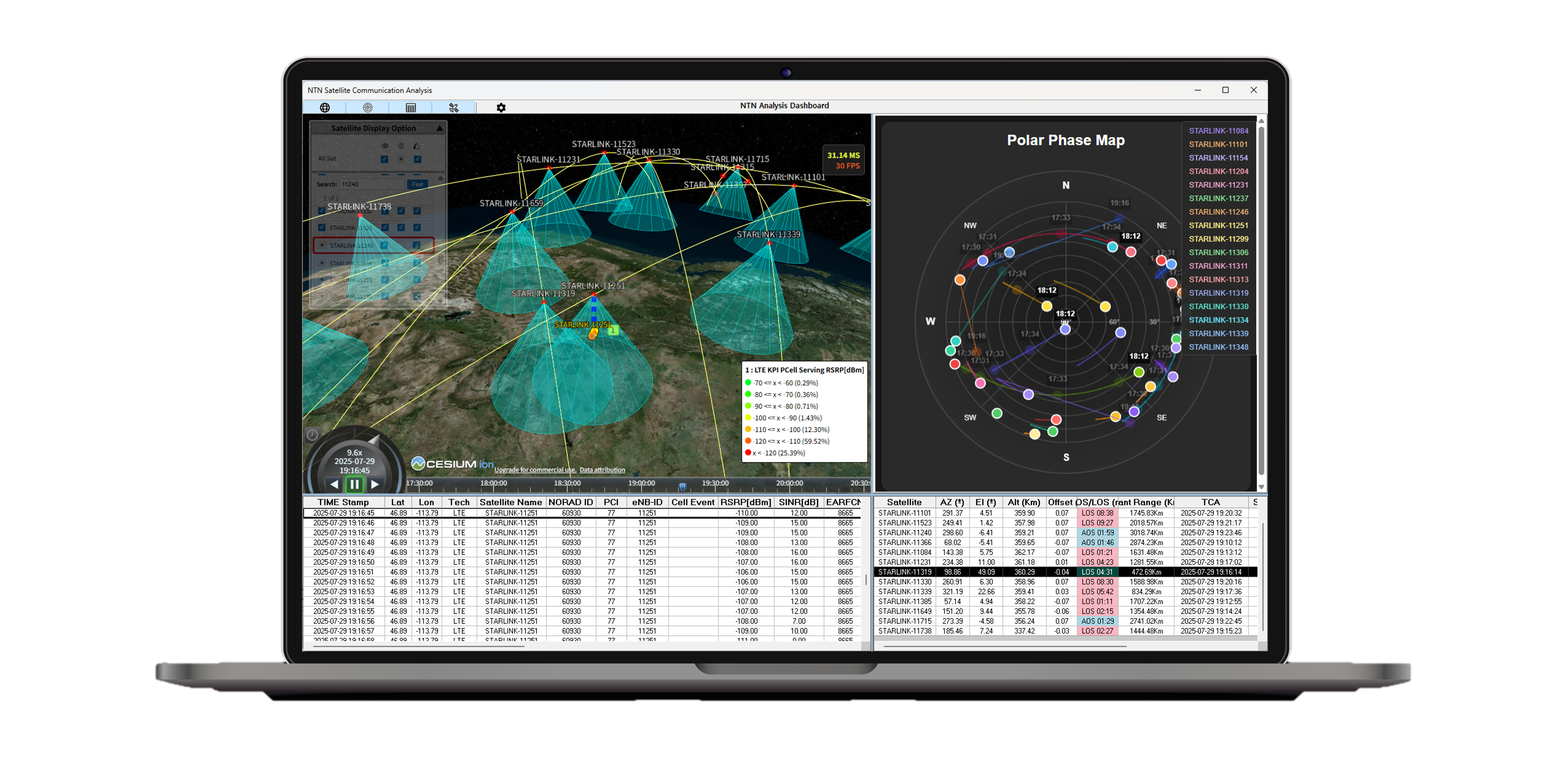
- 3D Satellite Map
2. 5G NTN Satellite Test Analysis
XCAP analyzes UE connectivity behavior as satellites enter and move through the field of view, identifying which satellite the UE was connected to at each moment and under what conditions connectivity was retained or lost. By correlating log data with time-varying satellite geometry, the analysis characterizes connectivity behavior under realistic D2C and satellite mobility scenarios.
Connectivity events such as service loss, RSRP degradation, and handover are aligned with satellite trajectory, enabling recurring event patterns to be identified along specific orbital segments rather than treated as isolated occurrences. This supports interpretation of UE connectivity behavior as a continuous process across a satellite pass.
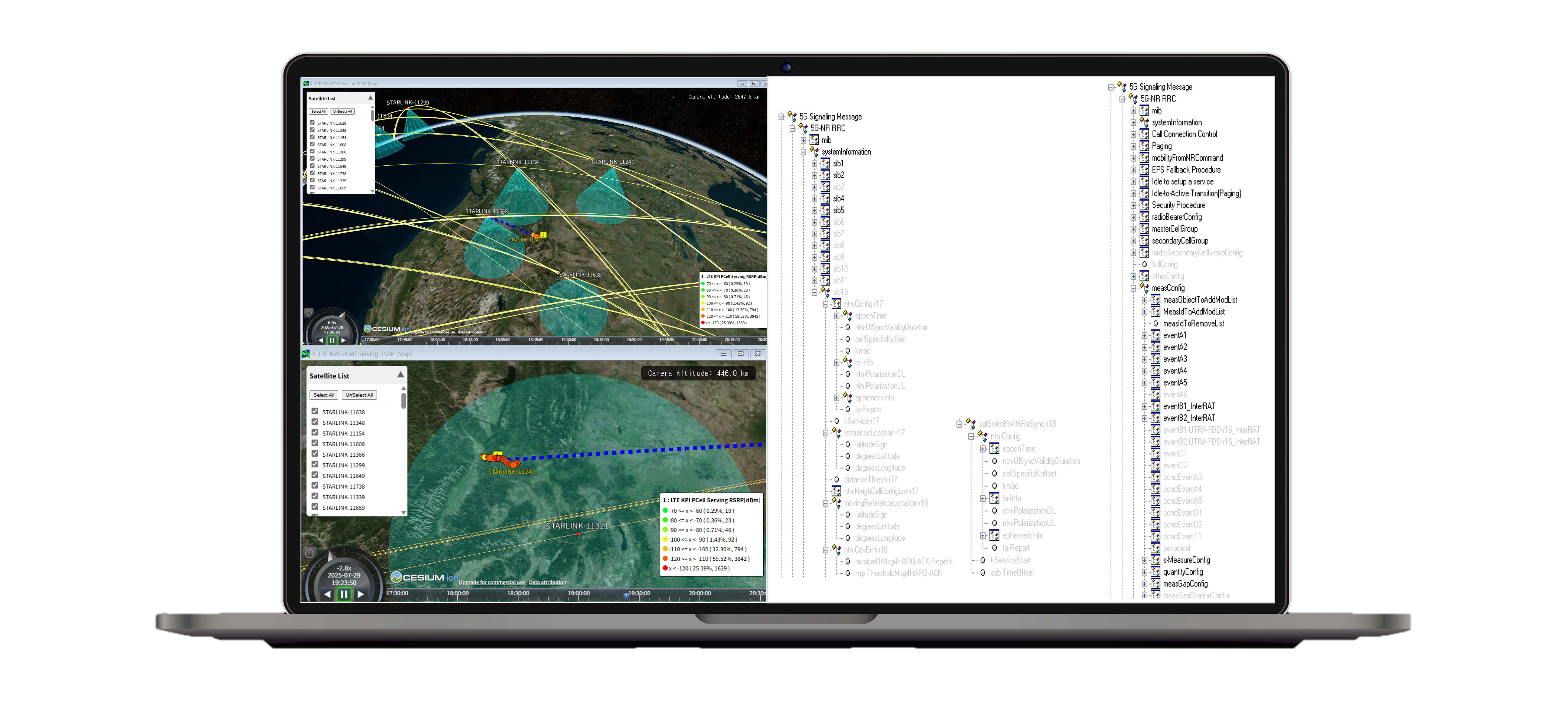
3. Doppler Effect Analysis
LEO satellites introduce significant Doppler frequency shifts due to high orbital velocity. XCAP provides dedicated analysis capabilities to evaluate Doppler variation and its impact on connectivity stability.
Doppler variation is analyzed as a function of satellite geometry, enabling differentiation between Doppler-induced effects and RF performance changes driven by propagation or environmental factors. Alignment of measured KPIs with TLE-based orbital models further allows comparison between expected and observed performance trends along a satellite pass.
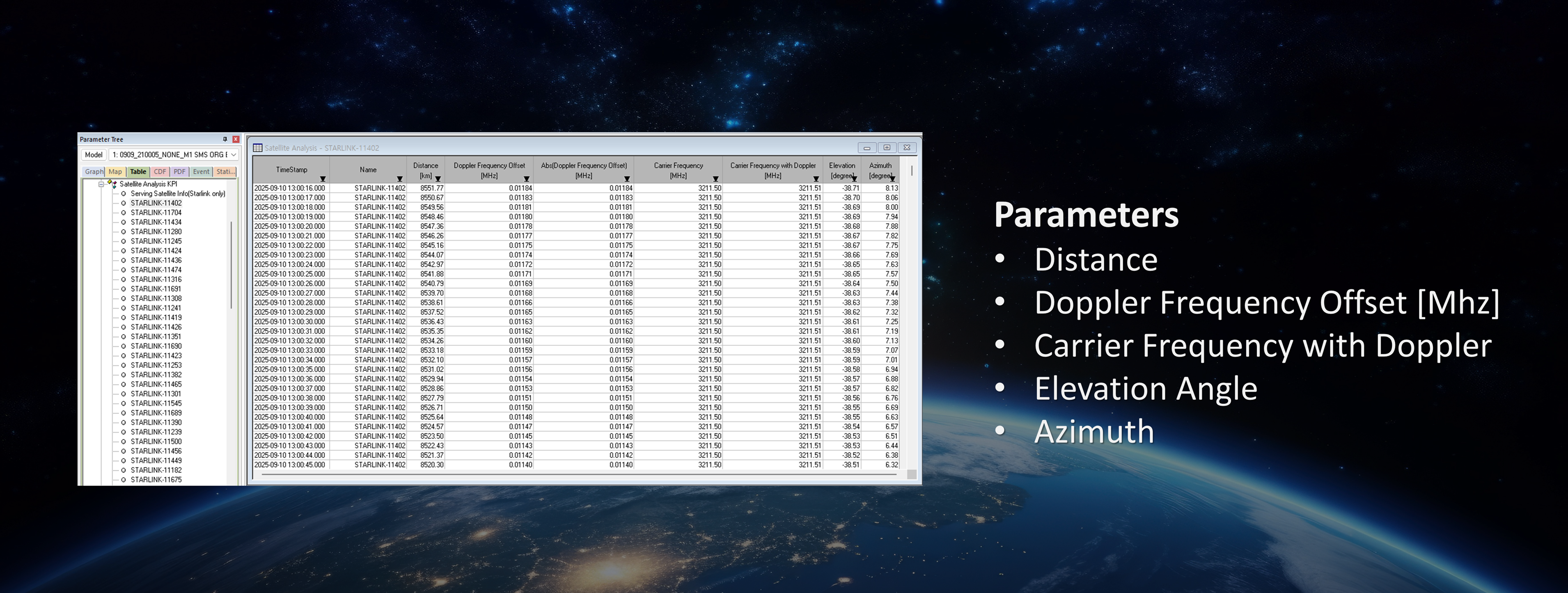
Conclusion
XCAP treats UE connectivity behavior in satellite-based networks as a function of orbital motion, geometry, and Doppler conditions rather than isolated KPI outcomes. This enables more precise interpretation of NTN and Direct-to-Cell connectivity characteristics, supporting condition-based understanding of connectivity behavior in dynamic satellite environments.